Koha alternatives
Koha is the most advanced open-source web-based Integrated Library System in use today by hundreds of libraries worldwide. Koha offers easy-to-use circulation policies, strong patron management, intuitive navigation, and extensive permissions for staff accounts, extensive support for holds, OPAC, staff, administrative features. The best Koha alternatives are: Evergreen, FOLIO
Here are the latest news about Koha:
15.06.23. Koha enhanced the Acquisitions module
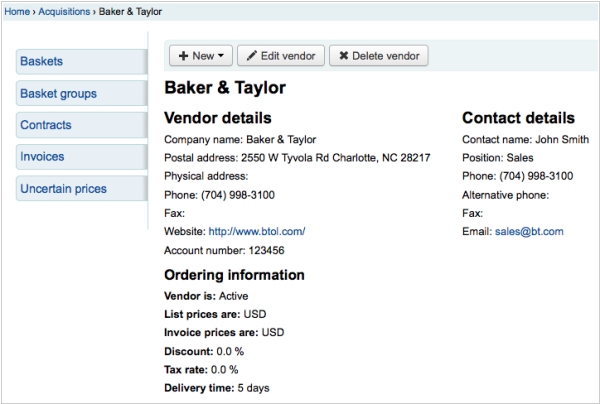
Free library management software Koha has updated the Acquisitions module that provides a way for the library to record orders placed with vendors and manage purchase budgets. The latest version introduces a modification to the order receive page, allowing users to select and process multiple orders simultaneously. This eliminates the need to reload the page or search for orders again after editing each one. A convenient 'Confirm' button is now available to receive all selected orders at once. This improvement paves the way for additional enhancements, such as implementing default actions on all selected orders. Furthermore, the new version introduces additional fields for order lines in the acquisition module. These fields provide the option to include user-defined information, which can be entered as free text or selected from predetermined lists of authorized values. It is also possible to extract information from the MARC record or create and edit a field within the MARC record.
2022. Koha adds Electronic resource management

The new version of open-source library management software Koha has added Electronic resource management (ERM) module. This new module adds a mechanism to track the selection, acquisition, licensing, access, maintenance, usage, evaluation, retention, and de-selection of a library’s electronic information resources. These resources include, but are not limited to, electronic journals, electronic books, streaming media, databases, datasets, CD-ROMs, and computer software. Also the new version adds option to require 2FA setup on first staff login, allows storing item values as a template for creating new items, adds ability to create bundles of items for circulation, adds the ability to create ‘saved searches’ for use as filters when searching the catalog.
2022. Koha enables two-factor authentication
The new version of ILS system Koha 22.05 introduces an optional initial implementation of two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance security during staff interface logins. This new feature incorporates time-based, one-time passwords (TOTP) as the second authentication factor. Librarians can utilize a dedicated application to manage the TOTP and obtain the necessary code for logging in. To enable 2FA for their account, librarians can navigate to More > Manage Two-Factor Authentication. The setup process involves the following steps: 1) Scan the QR code using an authenticator app. 2) Enter the generated one-time code. Subsequent logins will prompt librarians to enter the authenticator code after providing their regular login credentials. Any authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator, andOTP, and various others, can be utilized for this purpose. It is recommended to use applications that offer backup options for 2FA accounts, either through cloud-based or automatic methods.
2021. Koha improves Accounting and Transfers moduls
Koha, has released a major update that will be useful for small business and public libraries. The focus of this update was on refactoring the accounting code, with particular attention given to enhancing the 'Point of Sale' and 'Cash Management' features. These enhancements aim to improve the user interface by providing better access to cash-up functionality and facilitating auditing processes. Furthermore, efforts have been made to ensure that all actions related to account lines follow proper double-entry accounting methods, thereby establishing links between income and debts. A significant amount of work has been dedicated to refactoring the transfers system, resulting in improved maintainability and setting the stage for future enhancements. Notably, transfers can now be queued, and a priority system has been implemented for different mechanisms that trigger a transfer. Moreover, an audit trail has been implemented to enable easier debugging in the future. This has proven instrumental in resolving several long-standing bugs and addressing edge cases in the transfers process.
2007. LibLime acquires library management software Koha

LibLime has completed the acquisition of the Koha division from Katipo Communications Ltd, the original creators of Koha. The acquisition involved various assets, including existing support contracts with libraries that had partnered with Katipo, copyrights for the original Koha source code, and ownership of the koha.org domain and Website. LibLime has been offering commercial support for Koha since early 2005. This acquisition significantly bolsters LibLime's in-house development and support capabilities, empowering the company to meet the growing demand for open-source automation solutions in the library industry. Moreover, this acquisition exemplifies one of the distinct advantages of the open-source business and development model: customers of Katipo's Koha need not be concerned about transitioning to a new integrated library system (ILS).
15.06.23. Koha enhanced the Acquisitions module

Free library management software Koha has updated the Acquisitions module that provides a way for the library to record orders placed with vendors and manage purchase budgets. The latest version introduces a modification to the order receive page, allowing users to select and process multiple orders simultaneously. This eliminates the need to reload the page or search for orders again after editing each one. A convenient 'Confirm' button is now available to receive all selected orders at once. This improvement paves the way for additional enhancements, such as implementing default actions on all selected orders. Furthermore, the new version introduces additional fields for order lines in the acquisition module. These fields provide the option to include user-defined information, which can be entered as free text or selected from predetermined lists of authorized values. It is also possible to extract information from the MARC record or create and edit a field within the MARC record.
2022. Koha adds Electronic resource management

The new version of open-source library management software Koha has added Electronic resource management (ERM) module. This new module adds a mechanism to track the selection, acquisition, licensing, access, maintenance, usage, evaluation, retention, and de-selection of a library’s electronic information resources. These resources include, but are not limited to, electronic journals, electronic books, streaming media, databases, datasets, CD-ROMs, and computer software. Also the new version adds option to require 2FA setup on first staff login, allows storing item values as a template for creating new items, adds ability to create bundles of items for circulation, adds the ability to create ‘saved searches’ for use as filters when searching the catalog.
2022. Koha enables two-factor authentication

The new version of ILS system Koha 22.05 introduces an optional initial implementation of two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance security during staff interface logins. This new feature incorporates time-based, one-time passwords (TOTP) as the second authentication factor. Librarians can utilize a dedicated application to manage the TOTP and obtain the necessary code for logging in. To enable 2FA for their account, librarians can navigate to More > Manage Two-Factor Authentication. The setup process involves the following steps: 1) Scan the QR code using an authenticator app. 2) Enter the generated one-time code. Subsequent logins will prompt librarians to enter the authenticator code after providing their regular login credentials. Any authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator, andOTP, and various others, can be utilized for this purpose. It is recommended to use applications that offer backup options for 2FA accounts, either through cloud-based or automatic methods.
2021. Koha improves Accounting and Transfers moduls

Koha, has released a major update that will be useful for small business and public libraries. The focus of this update was on refactoring the accounting code, with particular attention given to enhancing the 'Point of Sale' and 'Cash Management' features. These enhancements aim to improve the user interface by providing better access to cash-up functionality and facilitating auditing processes. Furthermore, efforts have been made to ensure that all actions related to account lines follow proper double-entry accounting methods, thereby establishing links between income and debts. A significant amount of work has been dedicated to refactoring the transfers system, resulting in improved maintainability and setting the stage for future enhancements. Notably, transfers can now be queued, and a priority system has been implemented for different mechanisms that trigger a transfer. Moreover, an audit trail has been implemented to enable easier debugging in the future. This has proven instrumental in resolving several long-standing bugs and addressing edge cases in the transfers process.
2007. LibLime acquires library management software Koha

LibLime has completed the acquisition of the Koha division from Katipo Communications Ltd, the original creators of Koha. The acquisition involved various assets, including existing support contracts with libraries that had partnered with Katipo, copyrights for the original Koha source code, and ownership of the koha.org domain and Website. LibLime has been offering commercial support for Koha since early 2005. This acquisition significantly bolsters LibLime's in-house development and support capabilities, empowering the company to meet the growing demand for open-source automation solutions in the library industry. Moreover, this acquisition exemplifies one of the distinct advantages of the open-source business and development model: customers of Katipo's Koha need not be concerned about transitioning to a new integrated library system (ILS).
Add comment